Tracking marketing & campaign activity is very important for any business regardless of industry. Google Analytics tracks traffic to your website from two basic referring sources:
• organic – (direct, referral, search)
• paid
When a user reaches your website from either one of these sources, the user is tagged with a campaign tracking cookie identifying that source.
Campaign Tracking & Tagging URL’s
Campaign tracking in a broad sense can be referred to as a “method of identifying how users discover your site”. Webmasters & Marketers use campaign tracking in Google Analytics to accurately track online advertising campaigns to their websites, both from AdWords-generated campaigns as well as from other advertising sources.
Google Analytics automatically tracks all of the referrals and search queries that send traffic to your website. For example, each time someone is referred to your site, Analytics automatically captures the source, medium, keywords etc. In addition to getting information from referrals and queries that are tracked automatically, it is possible to customise links to your site. Customisation of links requires adding tags to the end of each URL.
Examples
http://www.example.com/?utm_campaign=spring&utm_medium=referral&utm_source=exampleblog
http://www.example.com/?utm_campaign=spring&utm_medium=email&utm_source=newsletter1
Separate the tags from a URL with a question mark. List the variables and values as pairs separated by an equals sign. Separate each variable-value pair with an ampersand.
To create unqiue custom URL’s, it is required to identify the following information for your campaign;
Campaign Source (utm_source)
Required. Use utm_source to identify a search engine, newsletter name, or other source.
Example: utm_source=google
Campaign Medium (utm_medium)
Required. Use utm_medium to identify a medium such as email or cost-per- click.
Example: utm_medium=cpc
Campaign Term (utm_term)
Used for paid search. Use utm_term to note the keywords for this ad.
Example: utm_term=running+shoes
Campaign Content (utm_content)
Used for A/B testing and content-targeted ads. Use utm_content to differentiate ads or links that point to the same URL.
Examples: utm_content=logolink or utm_content=textlink
Campaign Name (utm_campaign)
Used for keyword analysis. Use utm_campaign to identify a specific product promotion or strategic campaign.
Example: utm_campaign=spring_sale
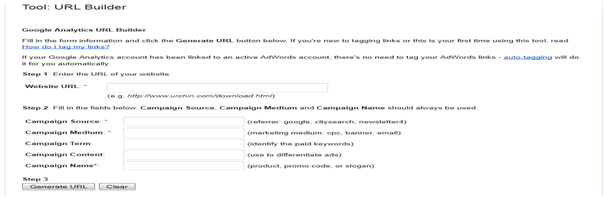
Creating Custom URL
In order to create custom URL with campaign tracking code, Google provide a tool called Google’s URL Builder and can be accessed by typing Google URL Builder into Google and clicking the first link.
In order for Analytics to display details about your PPC AdWords keywords you must either;
- Enable Destination URL auto-tagging. Google recommended this approach.
- Manually tag all keyword destination URLs with tracking variables. Google state you should only do this in the special cases.
How Auto-tagging Works
Auto-tagging automatically imports AdWords Data data into Analytics. When you enable auto-tagging, a parameter called gclid is added to your landing-page URL when a user clicks over to your site from an ad.
For example, if your site is www.mysite.com, when a user clicks on your ad it appears in the address bar as:
www.mysite.com/?gclid=123xyz
In addition, Analytics treats paid campaign visits from different sources as follows:
Source precedence—A direct traffic visit that follows a paid referred visit will never override an existing paid campaign. Whatever is the latest paid campaign visit is listed as the referral for the visit.
Campaign precedence—Each visit to your site from a different paid source—such as from a paid search engine link, an Adwords link, or a banner ad—overrides the campaign cookie information set by a previous source.
One Campaign Per Session—Each visit to your site from a different campaign—organic or paid—triggers a new session, regardless of the actual time elapsed in the current session. Specifically, a change in value for any of the following campaign URL parameters triggers a
new session: utm_source, utm_medium, utm_term, utm_content, utm_id, utm_campaign, gclid.
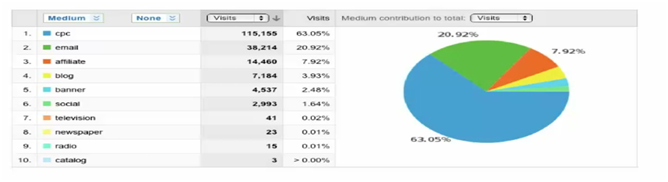
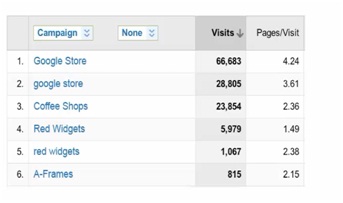
Analysing & Measuring Results
Once you have created and developed a custom URL tracking code, data in analytics will begin to compile and you will be able to view SEO, Off-line & Advertising results accordingly, as seen below;
Campaign tracking is very important and can be the difference between success and failure. So next time you are launching a campaign, you should be looking to utilise campaign tracking.





Connect With Us